Table of Contents
Introduction
Body Mass Index (BMI) is a widely used measure of body fat that is calculated based on a person’s weight and height. BMI is used as an indicator of overall health status and can help individuals and healthcare professionals assess the risk of weight-related health issues. Understanding your BMI can provide valuable insight into your health and well-being and can help you make informed decisions about diet, exercise, and other lifestyle factors.
In this guide, we’ll provide a comprehensive overview of what BMI is, how it’s calculated, and what the different BMI categories mean for your health. We’ll also cover the limitations of BMI as a measure of health, as well as the factors that can influence your BMI. By the end of this guide, you’ll have a better understanding of your own BMI and how it relates to your overall health and will be better equipped to make informed decisions about your health and well-being.
What is Body Mass Index (BMI)?
Body Mass Index (BMI) is a measure of body fat based on a person’s weight and height. BMI is calculated by dividing a person’s weight (in pounds) by the square of their height (in inches) and then multiplying times 703. The resulting number is then used to determine whether a person is underweight, normal weight, overweight, or obese.
Example: To calculate BMI for someone who is 5’11 & 180 lbs
BMI = (weight in pounds / (height in inches x height in inches)) x 703
180 lbs / (71 inches * 71 inches) * 703 = 25.10
Note: For your convenience, you can calculate your BMI through this online BMI Calculator available through the CDC.
BMI is a simple and widely used measure of body fat that can be used to screen for weight-related health issues. However, BMI is not a perfect measure of health. For example, a person with a high BMI may have a large amount of muscle mass, which could cause them to be classified as overweight or obese, even if they are in good health. Similarly, an older adult with a lower BMI may be at higher risk for health issues, despite being classified as normal weight.
Despite its limitations, BMI is a useful tool for assessing overall health status and identifying potential health risks. The BMI categories are as follows:
- Underweight: BMI less than 18.5
- Normal weight: BMI between 18.5 and 24.9
- Overweight: BMI between 25 and 29.9
- Obese: BMI 30 or higher
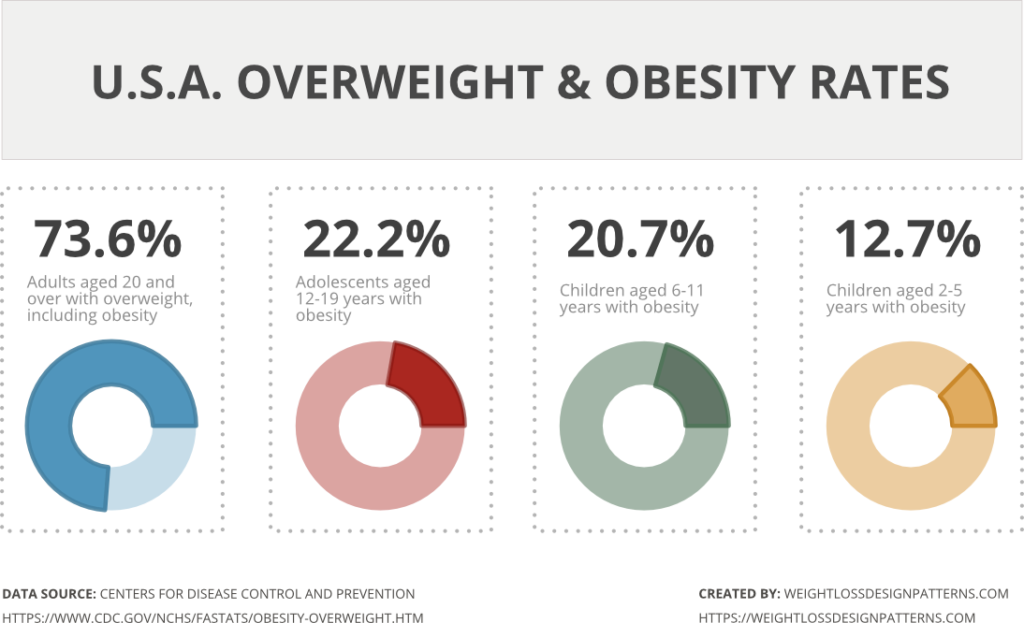
In the United States, the percentage of adults who are overweight or obese has been steadily increasing, with over 73% of adults falling into this category in 2017-2018. Additionally, childhood obesity is a growing concern, with nearly 1 in 5 children aged 6-19 being classified as obese. To better understand the scope of this issue, we’ve created an infographic that presents the latest data on obesity rates in the US, broken down by age group. Take a closer look to see how obesity rates vary across different age groups and to learn more about the health risks associated with being overweight or obese.”
What Your BMI Means
If your BMI falls outside of the normal weight range, it’s important to discuss your health status with a healthcare professional. Being underweight can mean your body isn’t getting the necessary nutrients it needs and can put you at risk for developing health issues related to malnutrition such as anemia or amenorrhea in women. Being overweight and obese increases your risk of many chronic diseases including hypertension, type-2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease. Be mindful of your BMI so you can take steps to improve it when needed, like eating healthier meals and exercising regularly.
Factors Affecting BMI
Body Mass Index (BMI) is an important number to understand when assessing overall health status. Genetics, age, gender, and lifestyle choices can all influence one’s BMI; however, adjusting these active decisions does not always lead to a change in BMI value. That said, understanding one’s BMI alongside other health metrics like body fat percentage and body composition provides a more inclusive measure of health status than using just BMI alone. For instance, athletes may experience higher Body Mass due to muscle over-fat gain without necessitating changes to their diet or activity level. Therefore adopting the 360-degree approach by taking Body Mass Index along with Body Fat Percentage and Body Composition is key to getting the most accurate picture of your health status.
Conclusion
Body Mass Index (BMI) is a useful tool for assessing overall health status and identifying potential health risks. Although BMI has its limitations, it can be used to screen for weight-related issues such as being underweight or overweight. It’s essential to understand the factors that affect your BMI in order to make informed decisions about your health and well-being. Taking an all-encompassing approach by considering Body Mass Index along with body fat percentage and body composition will provide you with more accurate information on your current state of health. With this knowledge, you’ll be better equipped to take steps towards improving your own physical condition if necessary.
If you’re interested in learning more about weight loss, consider checking out “A Programmer’s Design Patterns for Weight Loss,” this is my book that provides practical tips and strategies for achieving your weight loss goals. Remember that every person’s journey is unique, and with the right mindset and support, anyone can achieve their fitness goals.

